The first step in any optical manufacturing process is the selection of appropriate optical materials. Optical parameters (refractive index, Abbe number, transmittance, reflectivity), physical properties (hardness, deformation, bubble content, Poisson’s ratio), and even temperature characteristics (thermal expansion coefficient, relationship between refractive index and temperature) of optical materials All will affect the optical properties of optical materials. Performance of optical components and systems. This article will briefly introduce common optical materials and their properties.
Optical materials are mainly divided into three categories: Optical glass, optical crystal and Special optical materials.
 01 Optical Glass
01 Optical Glass
Optical glass is an amorphous (glassy) optical medium material that can transmit light. Light passing through it can change its propagation direction, phase and intensity. It is commonly used to produce optical components such as prisms, lenses, mirrors, windows and filters in optical instruments or systems. Optical glass has high transparency, chemical stability and physical uniformity in structure and performance. It has specific and accurate optical constants. In the low-temperature solid state, optical glass retains the amorphous structure of the high-temperature liquid state. Ideally, the internal physical and chemical properties of glass, such as refractive index, thermal expansion coefficient, hardness, thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, elastic modulus, etc., are the same in all directions, which is called isotropy.
The main manufacturers of optical glass include Schott of Germany, Corning of the United States, Ohara of Japan, and domestic Chengdu Guangming Glass (CDGM), etc.
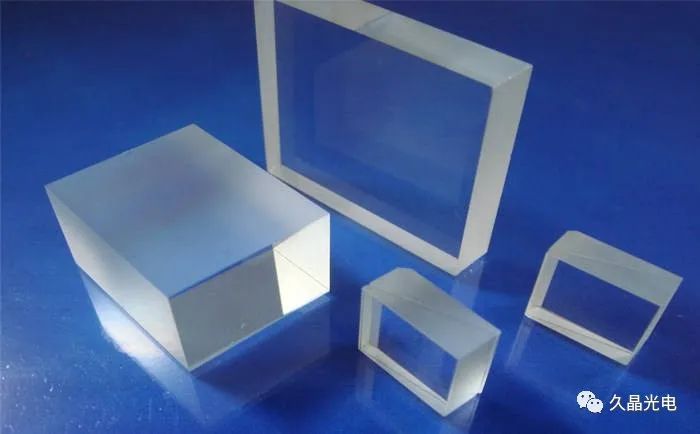
Refractive index and dispersion diagram
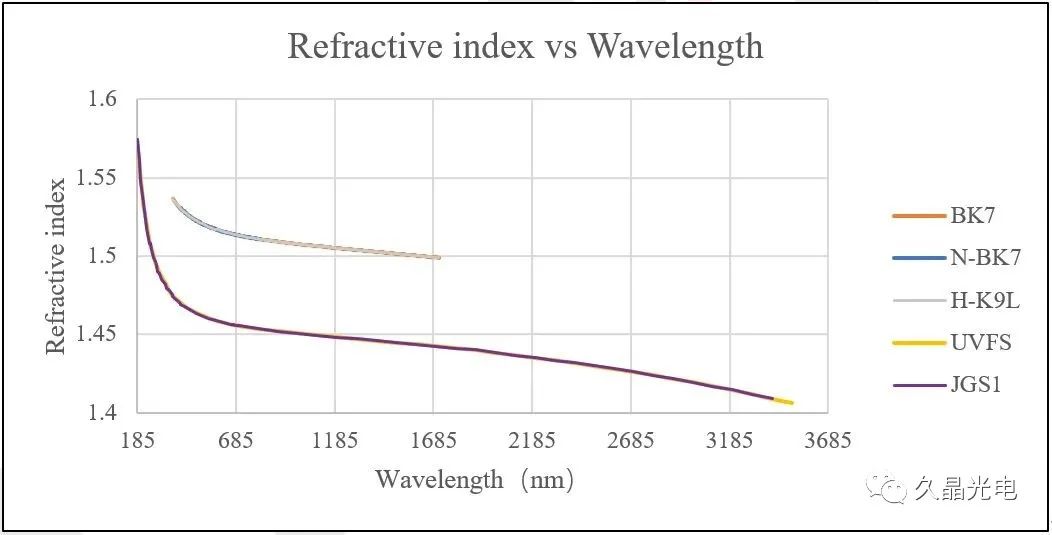
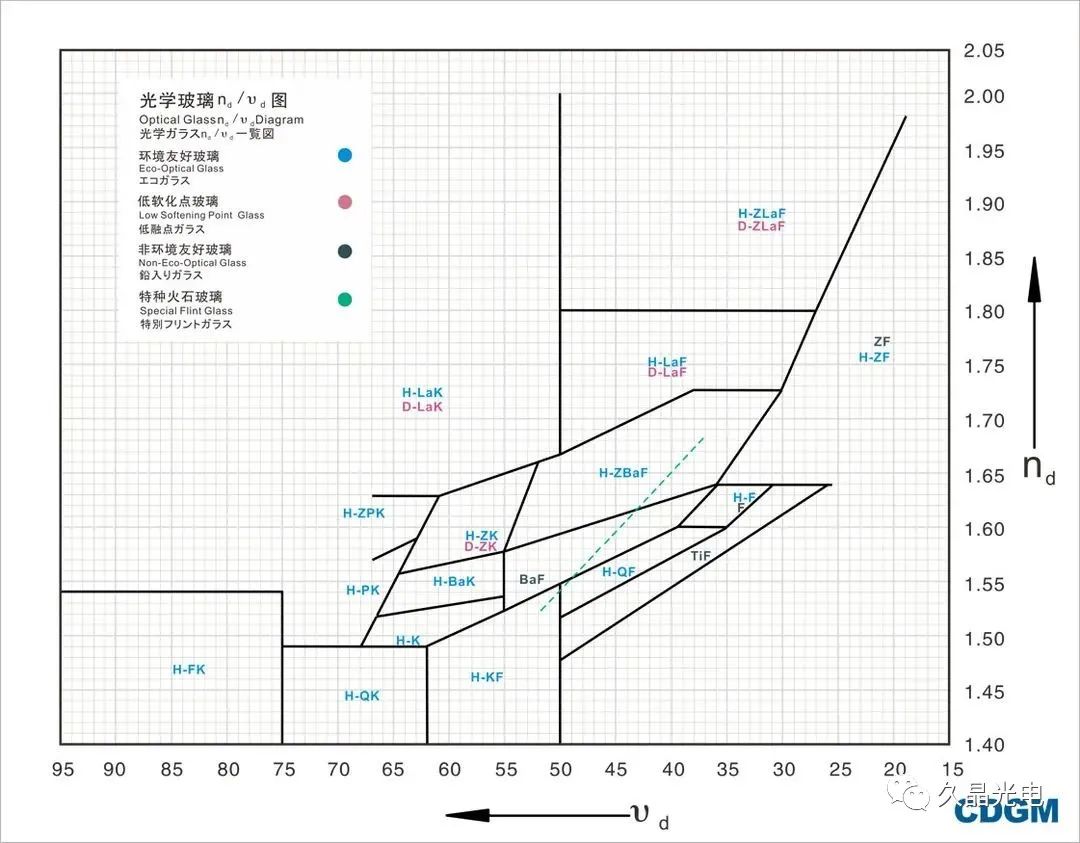
optical glass refractive index curves
02. Optical crystal
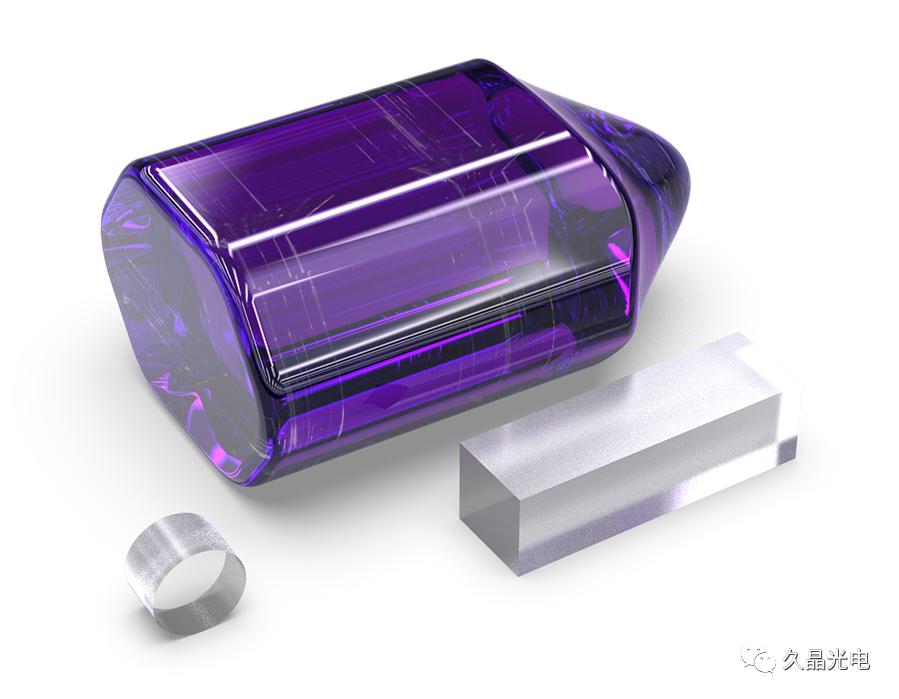
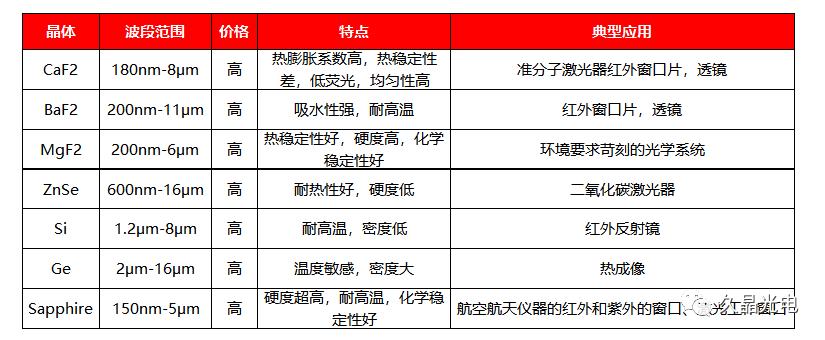
Optical crystal refers to the crystal material used in optical media. Due to the structural characteristics of optical crystals, it can be widely used to make various windows, lenses, and prisms for ultraviolet and infrared applications. According to the crystal structure, it can be divided into single crystal and polycrystalline. Single crystal materials have high crystal integrity and light transmittance, as well as low input loss, so single crystals are mainly used in optical crystals.
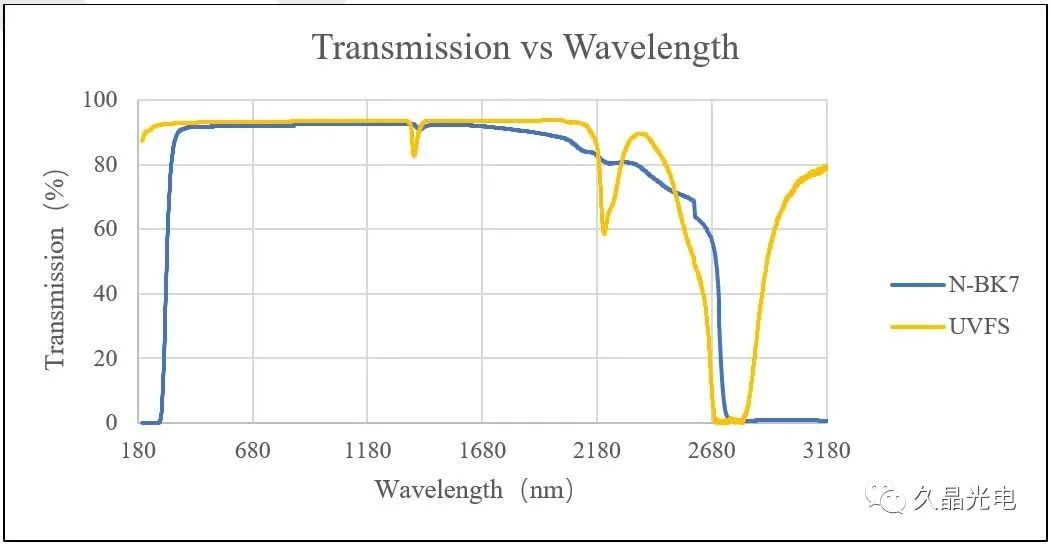
Specifically: Common UV and infrared crystal materials include: quartz (SiO2), calcium fluoride (CaF2), lithium fluoride (LiF), rock salt (NaCl), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), etc.
Polarizing crystals: Commonly used polarizing crystals include calcite (CaCO3), quartz (SiO2), sodium nitrate (nitrate), etc.
Achromatic crystal: The special dispersion characteristics of the crystal are used to manufacture achromatic objective lenses. For example, calcium fluoride (CaF2) is combined with glass to form an achromatic system, which can eliminate spherical aberration and secondary spectrum.
Laser crystal: used as working materials for solid-state lasers, such as ruby, calcium fluoride, neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet crystal, etc.
Crystal materials are divided into natural and artificially grown. Natural crystals are very rare, difficult to grow artificially, limited in size, and costly. Generally considered when glass material is insufficient, it can work in the non-visible light band and is used in the semiconductor and laser industries.
03 Special optical materials
a. Glass-ceramic
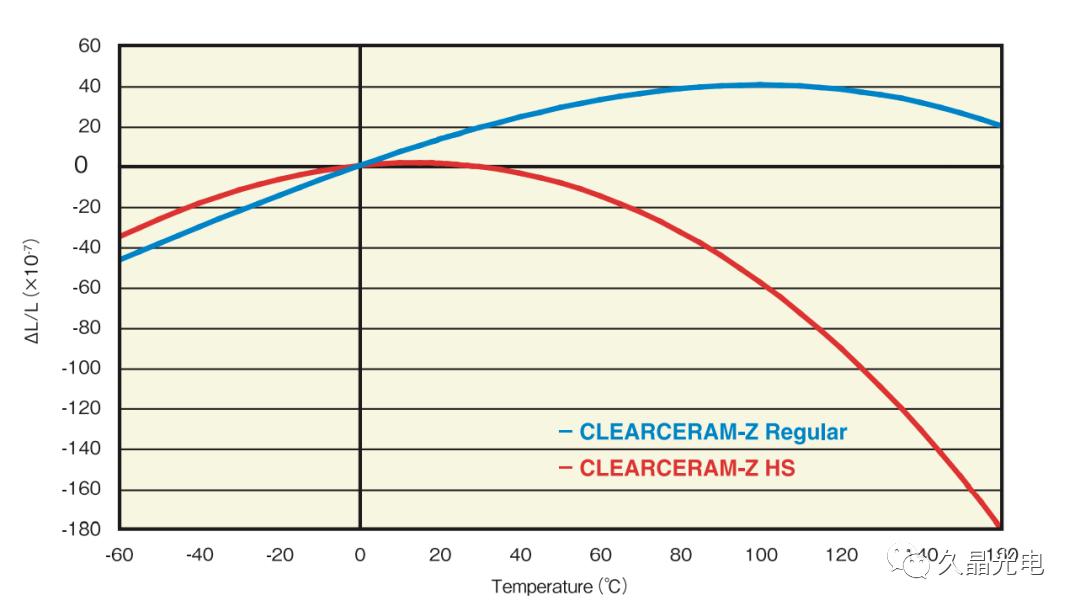
Glass-ceramic is a special optical material that is neither glass nor crystal, but somewhere in between. The main difference between glass-ceramic and ordinary optical glass is the presence of crystal structure. It has a finer crystal structure than ceramic. It has the characteristics of low thermal expansion coefficient, high strength, high hardness, low density, and extremely high stability. It is widely used in the processing of flat crystals, standard meter sticks, large mirrors, laser gyroscopes, etc.
The thermal expansion coefficient of microcrystalline optical materials can reach 0.0±0.2×10-7/℃ (0~50℃)
b. Silicon Carbide
Silicon carbide is a specialty ceramic material that is also used as an optical material. Silicon carbide has good stiffness, low thermal deformation coefficient, excellent thermal stability, and significant weight reduction effect. It is considered the main material for large-size lightweight mirrors and is widely used in aerospace, high-power lasers, semiconductors and other fields.
These categories of optical materials can also be called optical media materials. In addition to the major categories of optical media materials, optical fiber materials, optical film materials, liquid crystal materials, luminescent materials, etc. all belong to optical materials. The development of optical technology is inseparable from optical material technology. We look forward to the progress of my country’s optical material technology.
Post time: Jan-05-2024