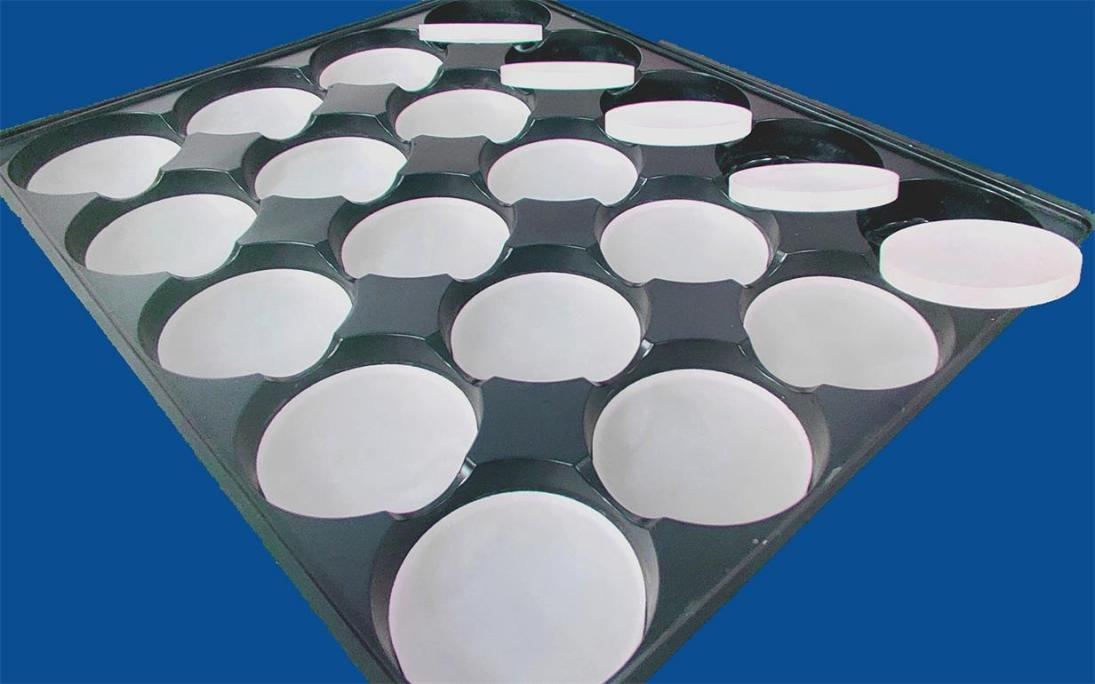
Optical glass was originally used to make glass for lenses.
This kind of glass is uneven and has more bubbles.
After melting at high temperature, stir evenly with ultrasonic waves and cool naturally.
It is then measured by optical instruments to check purity, transparency, uniformity, refractive index and dispersion.
Once it passes quality inspection, a prototype of the optical lens can be formed.
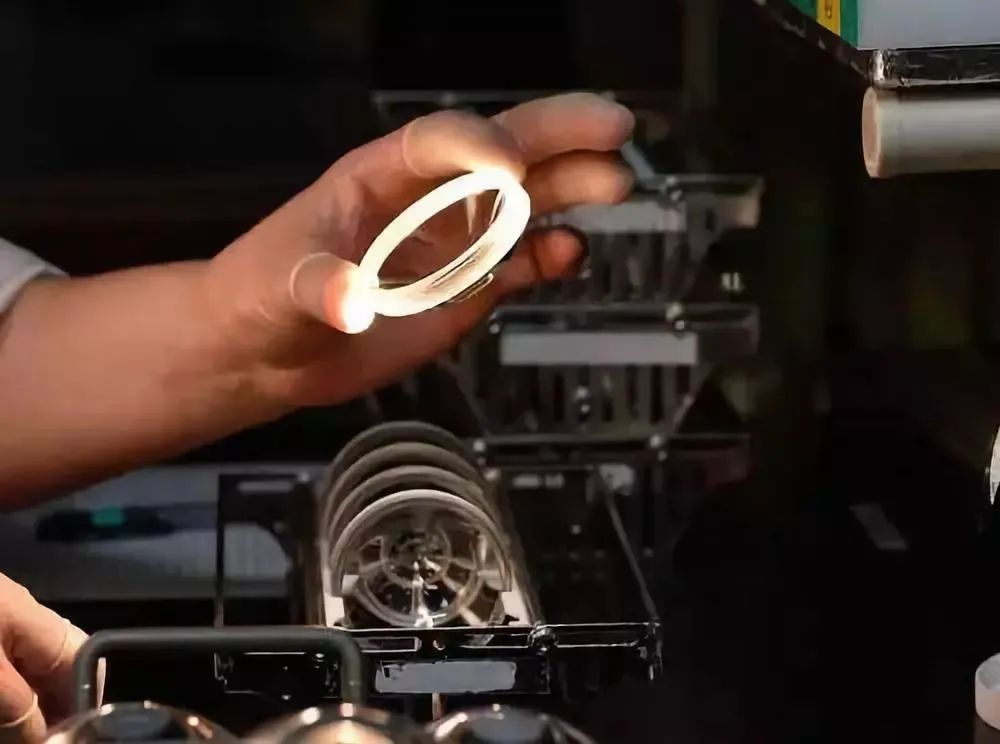

The next step is to milling the prototype, eliminate bubbles and impurities on the surface of the lens, achieving a smooth and flawless finish.

The next step is fine grinding. Remove the surface layer of the milled lens. Fixed thermal resistance (R-value).
The R value reflects the ability of the material to resist thinning or thickening when subjected to tension or pressure in a certain plane.
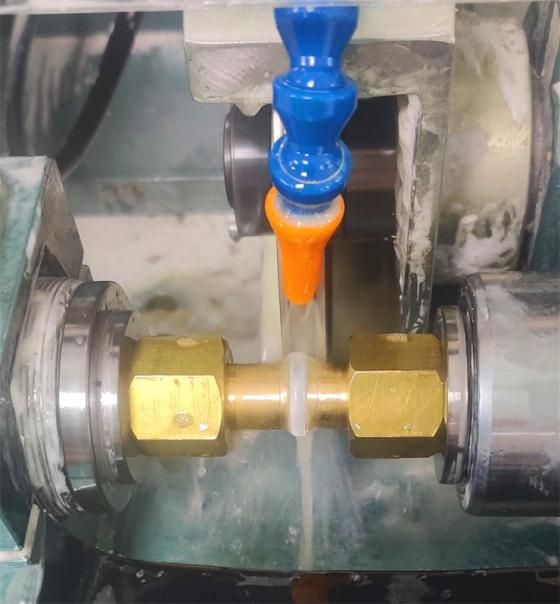

After grinding process, is centring edging process.
The lenses are edged from their original size to the specified outer diameter.
The followed process is polishing. Utilize appropriate polishing liquid or polishing powder, the fine ground lens is polished to make the appearance more comfortable and exquisite.
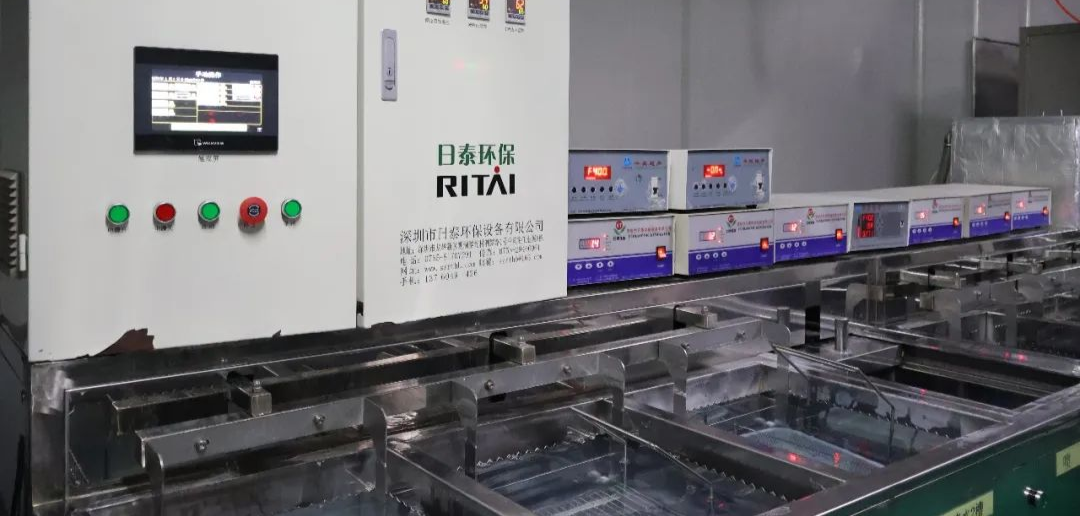


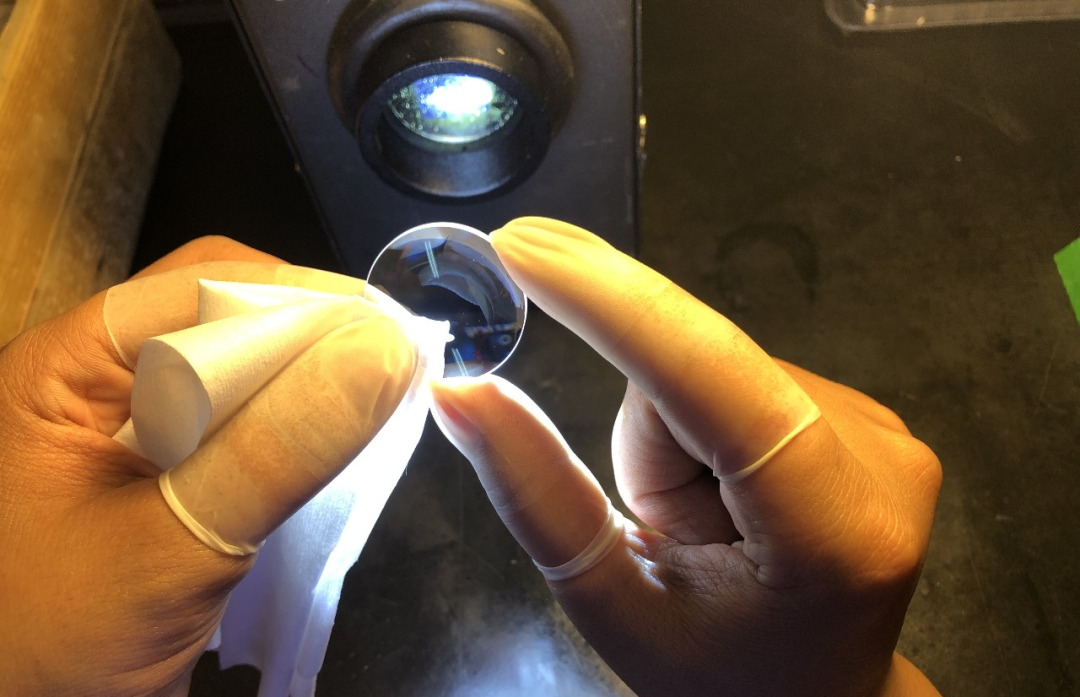
After polishing, the lens needs to be cleaned repeatedly to remove the remaining polishing powder on the surface. This is done to prevent corrosion and mold growth.
After the lens is completely dehydrated, it is coated according to manufacturing requirements.


Process of painting based on the lens specifications and whether an anti-reflective coating is needed. For lenses that require anti-reflective properties, a layer of black ink is applied to the surface.
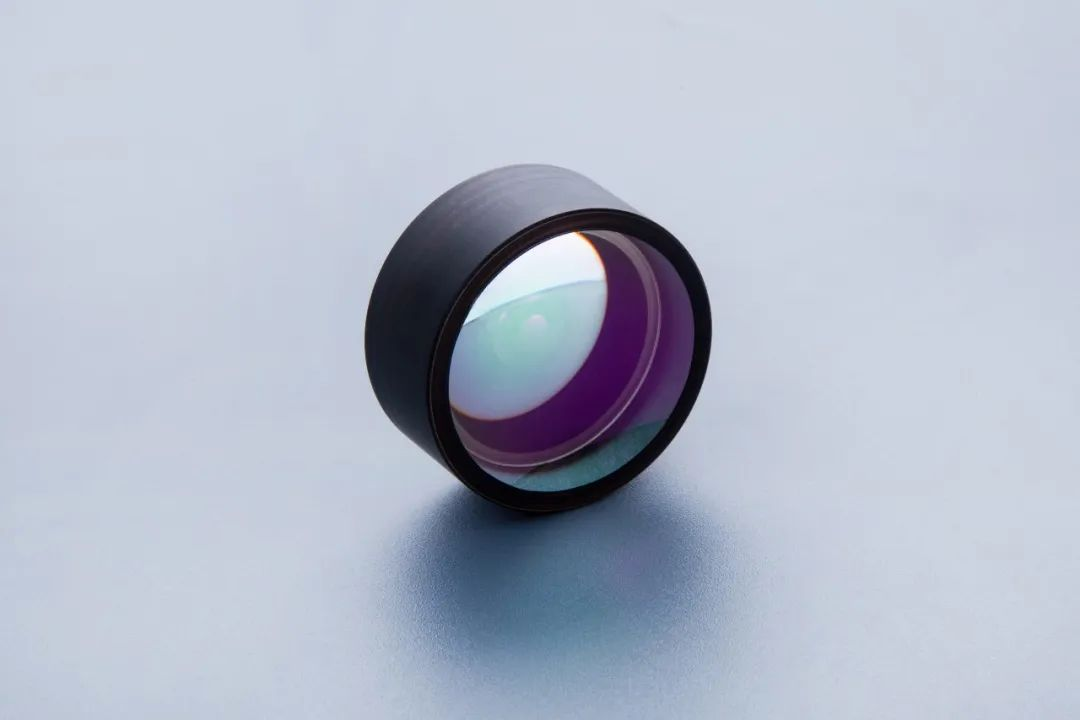

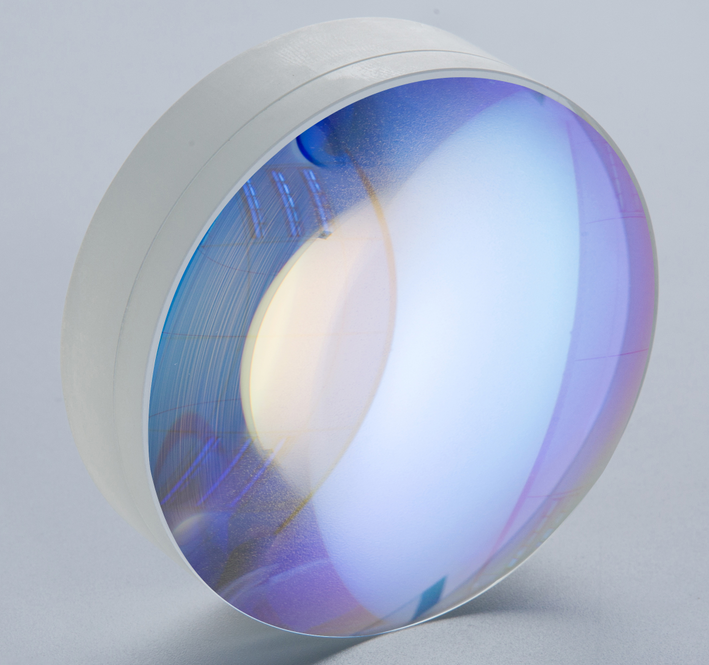
The final step is gluing, Make two lenses with opposite R-values and the same outer diameter bond.
Depending on the manufacturing requirements, the processes involved may vary slightly. However, the basic production process of qualified optical glass lenses is the same. It includes multiple cleaning steps followed by manual and mechanical precision grinding. Only after these processes can the lens gradually transform into the ordinary lens we see.

Post time: Nov-06-2023