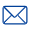
(Flow cytometry , FCM ) is a cell analyzer that measures the fluorescence intensity of stained cell markers. It is a high-tech technology developed based on the analysis and sorting of single cells. It can quickly measure and classify the size, internal structure, DNA, RNA, proteins, antigens and other physical or chemical properties of cells, and can be based on the collection of these classifications.

Flow cytometer mainly consists of the following five parts:
1 Flow chamber and fluidics system
2 Laser light source and beam shaping system
3 Optical system
4 Electronics, storage, display and analysis system
5 Cell sorting system
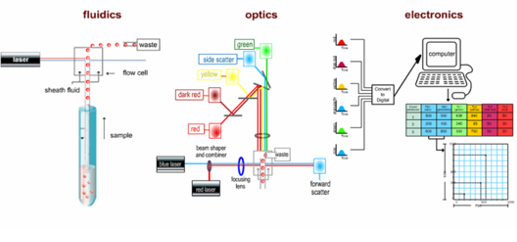
Among them, laser excitation in the laser light source and beam forming system is the main measurement of fluorescence signals in flow cytometry. The intensity of the excitation light and the exposure time are related to the intensity of the fluorescence signal. Laser is a coherent light source that can provide single-wavelength, high-intensity, and high-stability illumination. It is the ideal excitation light source to meet these requirements.
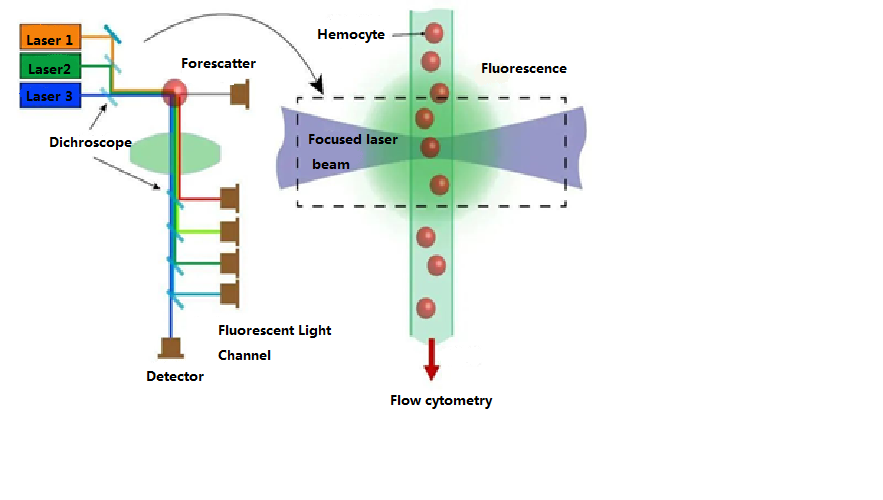
There are two cylindrical lenses between the laser source and the flow chamber. These lenses focus a laser beam with a circular cross-section emitted from the laser source into an elliptical beam with a smaller cross-section (22 μm × 66 μm). The laser energy within this elliptical beam is distributed according to a normal distribution, ensuring consistent illumination intensity for cells passing through the laser detection area. On the other hand, the optical system consists of multiple sets of lenses, pinholes, and filters, which can be roughly divided into two groups: upstream and downstream of the flow chamber.
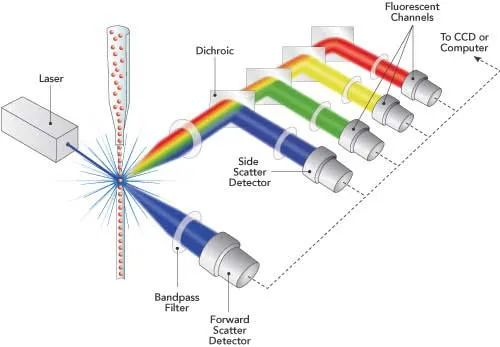
The optical system in front of the flow chamber consists of a lens and pinhole. The main function of the lens and pinhole (usually two lenses and a pinhole) is to focus the laser beam with a circular cross-section emitted by the laser source into an elliptical beam with a smaller cross-section. This distributes the laser energy according to a normal distribution, ensuring consistent illumination intensity for cells across the laser detection area and minimizing interference from stray light.
There are three main types of filters:
1: Long pass filter (LPF) - only allows light with wavelengths higher than a specific value to pass through.
2: Short-pass filter (SPF) - only allows light with wavelengths below a specific value to pass through.
3: Bandpass filter (BPF) - only allows light in a specific wavelength range to pass through.
Different combinations of filters can direct fluorescence signals at different wavelengths to individual photomultiplier tubes (PMTs). For example, filters for detecting green fluorescence (FITC) in front of PMT are LPF550 and BPF525. The filters used to detect orange-red fluorescence (PE) in front of the PMT are LPF600 and BPF575. The filters for detecting red fluorescence (CY5) in front of the PMT are LPF650 and BPF675.

Flow cytometry is mainly used for cell sorting. With the advancement of computer technology, the development of immunology and the invention of monoclonal antibody technology, its applications in biology, medicine, pharmacy and other fields are becoming increasingly widespread. These applications include cell dynamics analysis, cell apoptosis, cell typing, tumor diagnosis, drug efficacy analysis, etc.
Post time: Sep-21-2023